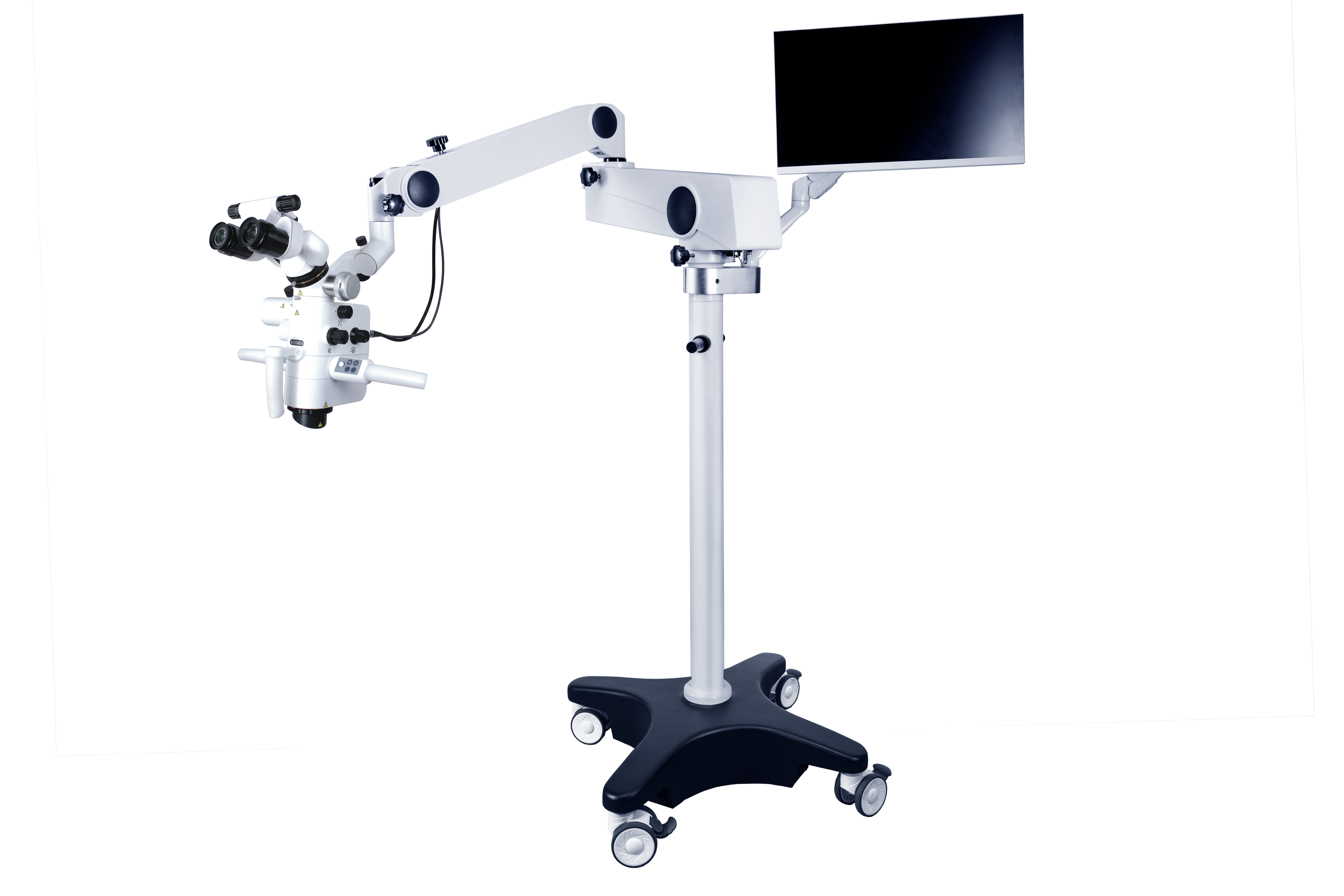
The role of surgical microscope in the diagnosis and treatment of pulp and periapical diseases
The excellent magnification and illumination functions of surgical microscopes not only help improve the quality of conventional root canal treatment, but also play an important role in the diagnosis and treatment of difficult cases of pulp and periapical diseases, especially in the management of complications in root canal treatment and periapical surgery, which cannot be replaced by other equipment. The structure and operation of dental surgical microscopes are relatively complex, and the proficiency of the operator may affect the evaluation of their clinical efficacy. This article evaluates the role of dental operating microscopes in the diagnosis and treatment of pulp and periapical diseases based on literature and clinical experience.
A dental surgical microscope consists of a precise optical system, a complex support system, and various accessories. In addition to being proficient in the operation of the dental operating microscope, surgeons usually need to perform mirror operations under an intraoral scope in non-surgical treatment of dental pulp diseases. Good hand eye coordination is also a skill that must be mastered in microsurgery. Blindly using a dental microscope without sufficient practice not only makes it difficult to achieve the expected results, but may also become a burden during treatment. Based on literature review and clinical experience, the author summarizes the role of Oral surgical microscopes in the diagnosis and treatment of pulp and periapical diseases, in order to provide guidance for the application of Oral operating microscopes in clinical diagnosis and treatment.
Using a Oral microscope during root canal treatment can provide a more intuitive and accurate understanding of the entire treatment process, while maximizing the preservation of dental tissue. The surgeon can clearly observe the fine structure of the pulp chamber and root canal, improve the cleaning and preparation effect of the root canal, and control the quality of root canal filling.
In clinical practice, besides pulp calcification, foreign bodies, fillings, and root canal wall steps are the most common causes of obstruction in the root canal. Under a surgical microscope, the surgeon can distinguish foreign objects and fillings that are different in color from the root canal wall. They can be removed using an ultrasonic file or a working tip to avoid excessive damage to the root canal structure and dental tissue.
For teeth with stepped root canal walls, the upper part of the stepped root canal can be cleaned and explored under a surgical microscope to confirm the bending direction of the root canal. A large taper opening file or ultrasonic working tip can be used to pre open the upper part of the root canal and observe and find the root canal. Use a small hand to pre bend with a file, dip the file tip in root canal lubricant and twist it slightly to explore the root canal. Once you cross the steps and enter the root canal, you can slightly lift the file until it can enter smoothly, and then replace it with a larger file to continue lifting. Rinse the root canal and rotate it until it is smooth.
Under the observation of a operating microscope, the depth and effectiveness of root canal irrigation can be observed, ensuring that the liquid is filled into each root canal of multiple teeth during the irrigation process, fully contacting the root canal wall and possible residual pulp tissue. Root canal preparation instruments are usually circular, and elliptical root canals are prone to debris accumulation in the gap area after being prepared by circular instruments. The isthmus of the C-shaped root canal system is also prone to residual pulp tissue and debris. Therefore, with the assistance of a surgical microscope, ultrasonic filing can be used to clean various parts of irregular root canals, observe the tissue structure and cleaning effect after cleaning.
During root canal filling, the surgical microscope can also provide excellent visual effects, allowing for observation and assistance in accurately delivering root canal sealants, dental crowns, etc. into each root canal. When hot tooth glue is vertically compressed and filled, it can be observed under a surgical microscope whether the glue has entered the irregular part of the root canal and whether it is in contact with the root canal wall. During the vertical pressurization process, it can also help control the force and depth of pressurization.
With the advancement of oral treatment equipment and materials, the treatment of pulp and periapical diseases may also develop from microsurgery to minimally invasive neurosurgery, similar to neurosurgery. More visualization devices have changed the surgeon's field of view and treatment methods. From the perspective of microtherapy, there is a need for surgical microscopes that are more suitable for oral treatment in the future, such as simpler and more stable stent systems, non-contact microscope adjustment systems, high-definition stereoscopic imaging systems, etc., in order to provide a more comfortable operating experience and wider application prospects for microtherapy of pulp and periapical diseases.

Post time: Jan-16-2025