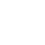
The use and maintenance of surgical microscopes
With the continuous progress and development of science, surgery has entered the era of microsurgery. The use of surgical microscopes not only allows doctors to see the fine structure of the surgical site clearly, but also enables various micro surgeries that cannot be performed with the naked eye, greatly expanding the scope of surgical treatment, improving surgical precision and patient cure rates. At present, Operating microscopes have become a routine medical device. Common Operating room microscopes include oral surgical microscopes, dental surgical microscopes, orthopedic surgical microscopes, ophthalmic surgical microscopes, urological surgical microscopes, otolaryngological surgical microscopes, and neurosurgical surgical microscopes, among others. There are slight differences in the manufacturers and specifications of surgical microscopes, but they are generally consistent in terms of operational performance and functional applications.
1 Basic structure of surgical microscope
Surgery generally uses a vertical surgical microscope (floor standing), which is characterized by its flexible placement and easy installation. Medical Surgical microscopes can generally be divided into four main parts: mechanical system, observation system, illumination system, and display system.
1.1 Mechanical System: High quality Operating microscopes are generally equipped with complex mechanical systems to fix and manipulate, ensuring that the observation and illumination systems can be quickly and flexibly moved to necessary positions. The mechanical system includes: base, walking wheel, brake, main column, rotating arm, cross arm, microscope mounting arm, horizontal X-Y mover, and foot pedal control board. The transverse arm is generally designed in two groups, with the aim of enabling the observation microscope to quickly move over the surgical site within the widest possible range. The horizontal X-Y mover can accurately position the microscope at the desired location. The foot pedal control board controls the microscope to move up, down, left, right, and focus, and can also change the magnification and reduction rate of the microscope. The mechanical system is the skeleton of a Medical operating microscope, determining its range of motion. When using, ensure the absolute stability of the system.
1.2 Observation System: The observation system in a general surgical microscope is essentially a variable magnification binocular stereo microscope. The observation system includes: objective lens, zoom system, beam splitter, program objective lens, specialized prism, and eyepiece. During surgery, assistants are often required to cooperate, so the observation system is often designed in the form of a binocular system for two people.
1.3 Lighting System: Microscope lighting can be divided into two types: internal lighting and external lighting. Its function is for certain special needs, such as ophthalmic slit lamp lighting. The lighting system consists of main lights, auxiliary lights, optical cables, etc. The light source illuminates the object from the side or top, and the image is generated by the reflected light entering the objective lens.
1.4 Display System: With the continuous development of digital technology, the functional development of operating microscopes is becoming increasingly rich. The surgical medical microscope is equipped with a television camera display and a surgical recording system. It can display the surgical situation directly on the TV or computer screen, allowing multiple people to observe the surgical situation simultaneously on the monitor. Suitable for teaching, scientific research, and clinical consultations.
2 Precautions for use
2.1 Surgical microscope is an optical instrument with complex production process, high precision, expensive price, fragile and difficult to recover. Improper use can easily cause huge losses. Therefore, before use, one should first understand the structure and usage of the Medical microscope. Do not rotate the screws and knobs on the microscope arbitrarily, or cause more serious damage; The instrument cannot be disassembled at will, as microscopes require high precision in assembly processes; During the installation process, strict and complex debugging is required, and it is difficult to restore if disassembled randomly.
2.2 Pay attention to keeping the Surgical microscope clean, especially the glass parts on the instrument, such as the lens. When liquid, oil, and blood stains contaminate the lens, remember not to use hands, cloths, or paper to wipe the lens. Because hands, cloths, and paper often have small pebbles that can leave marks on the mirror surface. When there is dust on the mirror surface, a professional cleaning agent (anhydrous alcohol) can be used to wipe it with a degreasing cotton. If the dirt is severe and cannot be wiped clean, do not forcefully wipe it. Please seek professional assistance to handle it.
2.3 The lighting system often contains extremely delicate devices that are not easily visible to the naked eye, and fingers or other objects should not be inserted into the lighting system. Careless damage will result in irreparable damage.
3 Maintenance of microscopes
3.1 The lifespan of the illumination bulb for the Surgical microscope varies depending on the working time. If the light bulb is damaged and replaced, be sure to reset the system to zero to avoid unnecessary losses to the machine. Every time the power is turned on or off, the lighting system switch should be turned off or the brightness adjusted to the minimum to avoid sudden high-voltage impact damaging the light source.
3.2 In order to meet the requirements of selecting the surgical site, field of view size, and clarity during the surgical process, doctors can adjust the displacement aperture, focal length, height, etc. through the foot pedal control board. When adjusting, it is necessary to move gently and slowly. When reaching the limit position, it is necessary to stop immediately, as exceeding the time limit may damage the motor and cause adjustment failure.
3.3 After using the microscope for a period of time, the joint lock may become too dead or too loose. At this time, it is only necessary to restore the joint lock to its normal working state according to the situation. Before each use of the Medical operating microscope, it is necessary to regularly check for any looseness in the joints to avoid unnecessary trouble during the surgical process.
3.4 After each use, use degreasing cotton cleaner to wipe off the dirt on the operating medical microscope, otherwise it will be difficult to wipe it clean for too long. Cover it with a microscope cover and keep it in a well ventilated, dry, dust-free, and non corrosive gas environment.
3.5 Establish a maintenance system, with professional personnel conducting regular maintenance checks and adjustments, necessary maintenance and repair of mechanical systems, observation systems, lighting systems, display systems, and circuit components. In short, caution should be exercised when using a microscope and rough handling should be avoided. To extend the service life of surgical microscopes, it is necessary to rely on the serious work attitude of the staff and their care and love for the microscopes, so that they can be in good operating condition and play a better role.
Post time: Jan-06-2025